- Chapter 1: Profiting from Deadly Products
In the global tobacco market, transnational tobacco companies (TTCs) have been shifting from developed countries and targeting markets in poorer, less developed countries where tobacco control is not as stringent and where tobacco use is significantly high among men and attractively low among women. In 2020, the tobacco market growth in ASEAN is projected to reach a total of 505.65 billion cigarettes sold, primarily in Indonesia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.- Profiting from Deadly Products
- Chapter 2: Nicotine and Tobacco Addiction
Globally, more than 1.1 billion people use tobacco, with adult male smokers (945 million) significantly outnumbering women (180 million). This alarming number represents about one-third of the global population aged 15 and above. It has grown substantially in low- and-middle-income countries (82% world’s smokers). In the ASEAN region, there are currently 122 million adult smokers, half of whom live in Indonesia (65 million).- Nicotine and Tobacco Addiction
- Chapter 3: Basic Needs Sacrificed
Tobacco use is inextricably linked to poverty. Tobacco consumption varies according to socioeconomic group, but in most countries, those who tend to consume tobacco the most are the poor and the poorest and men with low education.- Basic Needs Sacrificed
- Chapter 4: Burden of Death, Disease and Disability
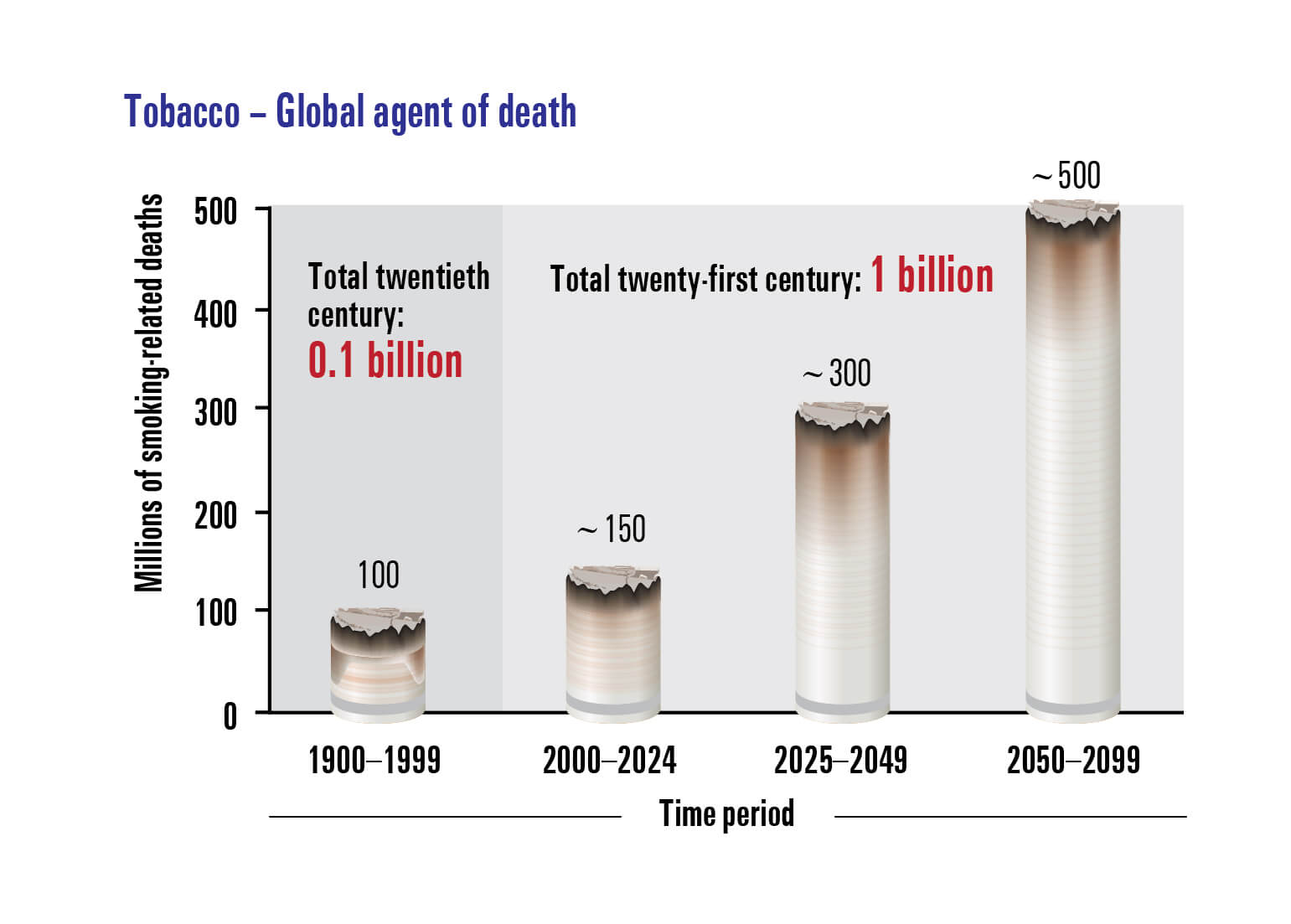
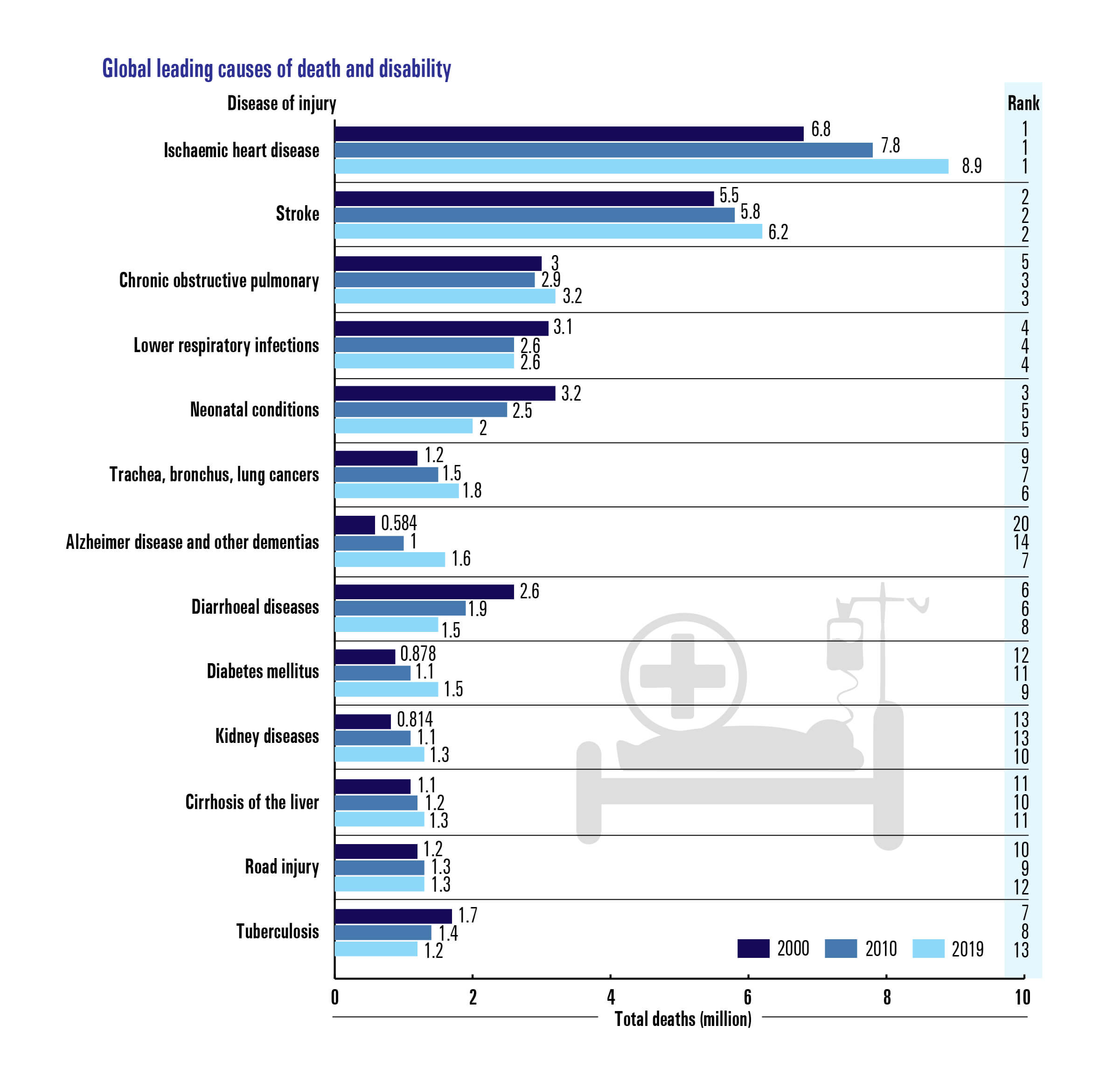
When used as intended by the manufacturer, tobacco is the only legal product that kills up to two thirds of its regular users, currently killing more than 7 million people globally each year, including about 890,000 non-smokers, who lose their lives due to exposure to secondhand smoke. As such, tobacco use continues to be the world’s single largest preventable cause of diseases, harming almost every organ of the body.- Burden of Death, Disease and Disability
- Chapter 5: Human and Financial Resources for Tobacco Control
Knowledgeable and skilled human resources and effective multi-sectoral collaboration at different levels of government and society are necessary for effective development and implementation of a wide range of tobacco control activities. To this end, the WHO FCTC requires Parties to establish or reinforce and finance a national coordinating mechanism or focal point in order to develop, implement, periodically update, and review comprehensive multi-sectoral national tobacco control strategies, plans and programmes (Articles 5.1 and 5.2).- Human and Financial Resources for Tobacco Control
- Chapter 6: Insulating Public Health Policies from Industry Interference
The tobacco industry is not like any other business. Despite selling a highly addictive and inherently defective product that kills up to two thirds of its consumers, it continues to escape commensurately stringent regulation of its business and products by interfering at all levels of tobacco control policy development and implementation. Through both overt and covert means, the industry uses its massive resources to deter and thwart governments' efforts to protect public health policies. Tobacco industry interference remains a major problem in the ASEAN region as in other parts of the world.- Insulating Public Health Policies from Industry Interference
- Chapter 7: Reducing Tobacco Affordability and Consumption
Excise tax increases that significantly raise tobacco product prices and reduce their affordability are among the most effective fiscal measures to reduce tobacco consumption (and thereby its adverse health consequences) by discouraging purchase of tobacco products, thereby encouraging tobacco cessation and preventing tobacco uptake among various segments of the population, in particular price-sensitive young people and the poor.- Reducing Tobacco Affordability and Consumption
- Chapter 8: Clearing the Air for a Healthier Environment
Secondhand smoke (SHS) kills, and WHO and other health authorities have declared that there is no safe level of exposure to SHS. Non-smokers exposed to SHS are equally at risk of tobacco-related diseases and premature death as those who actively smoke.- Clearing the Air for a Healthier Environment
- Chapter 9: A Picture is Worth a Thousand Words
Tobacco packaging serves as the most cost-effective communications channel for governments to convey health risks associated with tobacco use. Especially among those with low literacy levels, pictorial health warnings (PHWs) are an effective health promotion tool to increase awareness of tobacco’s harmful effects with no costs to government.- A Picture is Worth a Thousand Words
- Chapter 10: Pulling the Plug on Tobacco Marketing and Tobacco Philanthropy
To maximize profits, the tobacco industry invests billions of dollars yearly around the globe on tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship (TAPS) to aggressively promote its deadly products and the social acceptability of tobacco use. A wide range of TAPS strategies are employed to directly and indirectly make tobacco products attractive and pervasive, targeting not only potential tobacco users (i.e. youth, who are highly receptive to tobacco marketing) and current and former tobacco users, but also policy makers and the public, so as to artificially create the impression that tobacco use is normal and non-harmful or that the tobacco industry is a socially responsible corporate sector.- Pulling the Plug on Tobacco Marketing and Tobacco Philanthropy
- Chapter 11: Protecting Future Generations from Nicotine Addiction
Youth smokers, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, are a huge potential market for industry’s future growth. Tobacco companies target children and youths, whom they refer to as “replacement smokers” to replace older smokers who either quit or die from tobacco-related diseases. Youth smoking therefore remains the front line of the tobacco epidemic, as youths are more susceptible to tobacco marketing, and nicotine addiction is more entrenched in the developing adolescent brain. On average, most smokers start smoking before the age of 20.- Protecting Future Generations from Nicotine Addiction
- Chapter 12: Alternative Livelihood for Tobacco Growers
In recent decades, transnational tobacco companies have shifted tobacco leaf cultivation from high-income to low-income countries, where 90% of tobacco farming now takes place. Eight of the ten ASEAN countries, excluding Singapore and Brunei, are engaged in tobacco cultivation on different scales. About 329,606 hectares of land was used for tobacco farming across the region between 2014 and 2017.- Alternative Livelihood for Tobacco Growers